Long COVID: Understanding, Managing, and Recovering from Post-COVID Syndrome
As the world continues to navigate the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, a new health challenge has emerged: Long COVID. This condition affects a significant number of individuals who have recovered from the acute phase of COVID-19 but continue to experience persistent symptoms. In this article, we delve into what Long COVID is, its symptoms, management strategies, and recovery tips.
What is Long COVID?
Long COVID, also known as Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), refers to a range of symptoms that persist for weeks or months after the initial COVID-19 infection has cleared.These symptoms can affect various systems in the body and may fluctuate or relapse over time.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Long COVID is characterized by a wide array of health problems that can last four or more weeks after first being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19.
Common Symptoms of Long COVID
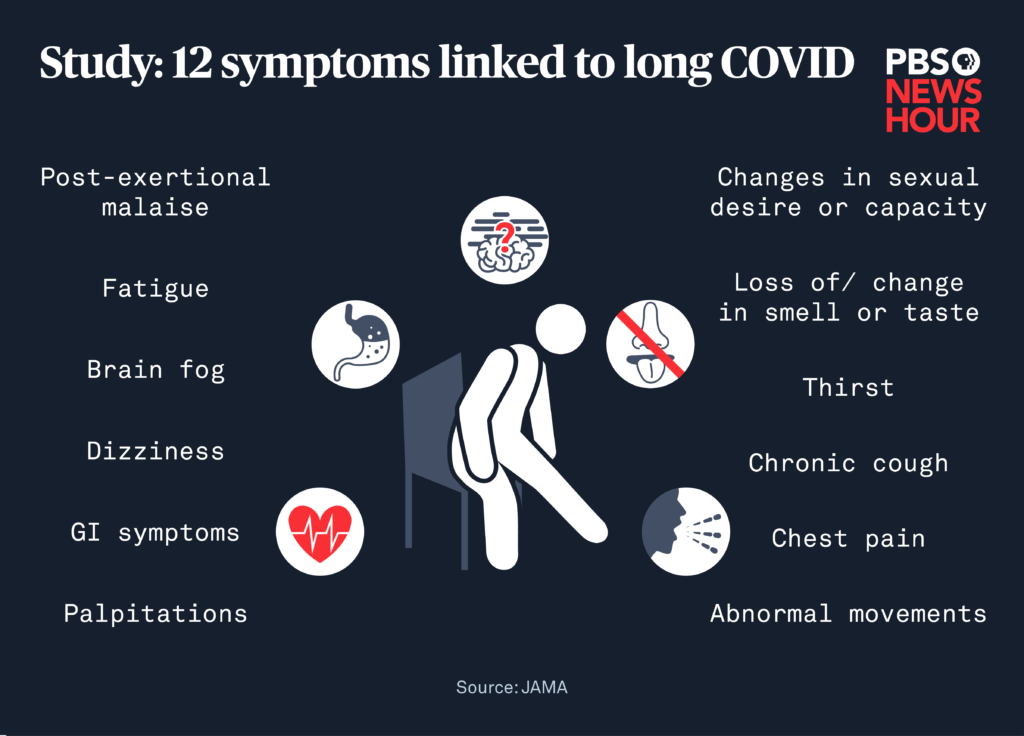
Long COVID manifests differently among individuals, but some commonly reported symptoms include:
- Fatigue: A persistent sense of tiredness or exhaustion that interferes with daily activities. CDC+1Health Information and Services+1
- Brain Fog: Difficulty with thinking, concentration, memory, or decision-making.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling short of breath during minimal exertion. British Heart Foundation+1The Irish Sun+1
- Joint and Muscle Pain: Ongoing discomfort in muscles or joints.
- Chest Pain: Persistent chest discomfort or pain. CDC+20NHS Inform+20Health Information and Services+20
- Cough: A lingering cough that doesn't go away.
- Loss of Taste or Smell: Continued loss or alteration of taste and smell. theaustralian
- Depression and Anxiety: Mental health challenges, including feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or anxiety.
It's important to note that these symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, and new symptoms may emerge over time. CDC
Who is at Risk?
Long COVID can affect anyone who has had COVID-19, regardless of the severity of their initial infection. However, certain factors may increase the risk:
- Severity of Initial Infection: Individuals who experienced severe COVID-19 symptoms or were hospitalized are more likely to develop Long COVID.
- Pre-existing Health Conditions: Those with underlying health issues, such as diabetes or cardiovascular diseases, may be at higher risk.
- Age and Gender: Some studies suggest that middle-aged women are more susceptible to Long COVID. theaustralian
Managing Long COVID Symptoms
While there is no one-size-fits-all treatment for Long COVID, several strategies can help manage symptoms:
1. Medical Consultation
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are crucial. They can help monitor symptoms, rule out other conditions, and provide referrals to specialists if needed.
2. Physical Rehabilitation
Engaging in tailored physical therapy can aid in regaining strength and endurance. It's essential to start slowly and increase activity levels gradually to avoid exacerbating symptoms.
3. Mental Health Support
Addressing mental health is vital. Counseling, therapy, and support groups can provide coping mechanisms and emotional support. theaustralian
4. Nutrition and Hydration
Maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated can support overall health and recovery. Some individuals find that certain dietary adjustments help alleviate specific symptoms.
5. Sleep Hygiene
Establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a restful environment can improve sleep quality, which is often disrupted in Long COVID patients.
Recovery Tips for Long COVID
Recovery from Long COVID is a gradual process. Here are some tips to aid in the journey:
- Pace Yourself: Avoid overexertion. Listen to your body and rest when needed.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break tasks into manageable steps and celebrate small achievements.
- Stay Connected: Engage with support groups or communities to share experiences and gain insights. Mayo Clinic Connect
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep a journal to track symptoms, triggers, and improvements.
- Seek Professional Help: Don't hesitate to consult healthcare providers for persistent or worsening symptoms.

Support Resources
Several organizations and platforms offer resources and support for individuals dealing with Long COVID:
- Mayo Clinic Post-COVID Recovery Group: An online community for sharing experiences and obtaining information. Mayo Clinic Connect
- Long COVID Alliance: A coalition providing resources and advocating for research and support. Long-COVID Alliance
- Survivor Corps: A grassroots movement connecting COVID-19 survivors with research and support networks. Mayo Clinic News Network+9Survivor Corps+9Long-COVID Alliance+9
- Downloadable Brochure: A full-color graphic to easily see Long Covid symptoms.
Conclusion
Long COVID presents a complex set of challenges that require a comprehensive and individualized approach to management and recovery. By staying informed, seeking appropriate medical care, and utilizing available resources, individuals can navigate the path to recovery more effectively.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of Long COVID, it's essential to consult healthcare professionals and explore support options to aid in the recovery journey.
Dr. Dombroski has been treating Long Covid patients with great success for several years now. Many of his patients have gone from being bedridden to living healthy lives.
Call or contact our office today and see how he can help you or a loved one recover from Long Covid and live the life you are meant to live!
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for medical guidance tailored to your situation.